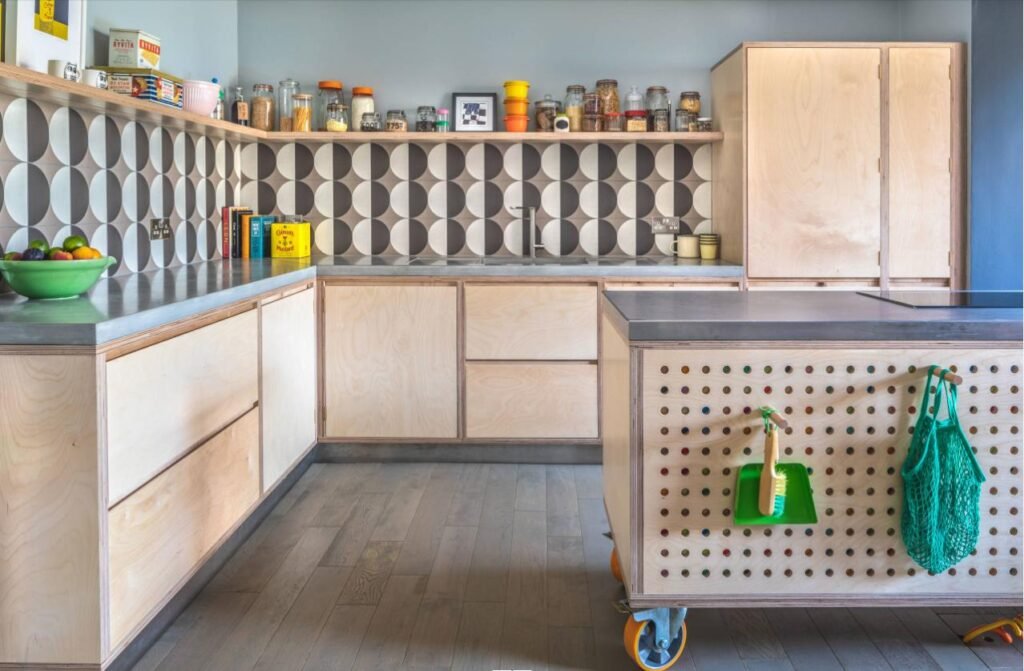
The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Plywood Furniture
Plywood furniture offers several advantages and disadvantages, which can influence your decision when choosing it for your home or projects.
Here are some of the key pros and cons of plywood furniture:
Advantages of Plywood Furniture:
- Strength and Durability: Plywood is engineered to be strong and stable. It is less prone to warping, cracking, or splitting compared to solid wood. This makes plywood furniture highly durable and suitable for long-term use.
- Cost-Effective: Plywood is often more affordable than solid wood, hardwoods in particular. It allows you to achieve a similar look and functionality without the high cost of solid wood furniture.
- Stability: The cross-grain construction of plywood, with alternating layers, provides stability and resistance to expansion and contraction due to changes in temperature and humidity.
- Versatility: Plywood can be easily cut and shaped into various designs and forms. It’s highly versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of furniture styles and applications.
- Available in Different Grades: Plywood comes in various grades, from low-grade utility panels to high-quality furniture-grade sheets. You can choose the grade that best suits your budget and aesthetic preferences.
- Lightweight: Plywood is lighter than many other materials used in furniture construction, making it easier to move and transport.
- Environmental Benefits: Some plywood is made from sustainable and responsibly harvested wood sources. Additionally, plywood can be more resource-efficient than solid wood, as it uses thinner veneers.

Disadvantages of Plywood Furniture:
- Aesthetics: Plywood has a distinct layered appearance, which may not appeal to everyone’s aesthetic preferences. Some people prefer the natural look of solid wood.
- Edge Finish: The edges of plywood furniture can have a layered or unfinished look. While some designs embrace this, others may require edge banding or other finishing techniques for a polished appearance.
- Quality Variability: The quality of plywood can vary depending on the manufacturer and grade. Low-quality plywood may have voids or irregularities, affecting its appearance and structural integrity.
- Moisture Sensitivity: While plywood is more moisture-resistant than some other materials, it can still be susceptible to damage if exposed to excessive moisture or humidity. Proper finishing and sealing are essential to protect plywood from moisture.
- Not Ideal for Heavy Loads: While plywood is strong, it may not be as suitable for extremely heavy loads or structural components as solid wood or other materials.
- Environmental Concerns: Some plywood products may use adhesives that contain formaldehyde, which can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It’s essential to check for eco-friendly and low-VOC options if environmental concerns are a priority.
In summary, plywood furniture offers strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for various applications. However, its appearance may not suit all design preferences, and the quality can vary. Commonly used types of plywood are 3-plywood, 13-plywood and so on. Plywood may improve wood utilisation and is an important strategy to save wood. The standard length and width specifications are: 1220x2440mm, and the thickness specifications are: 3, 5, 9, 12, 15, 18mm, and so on. The most common tree species are camphor, willow, poplar, eucalyptus, and others.