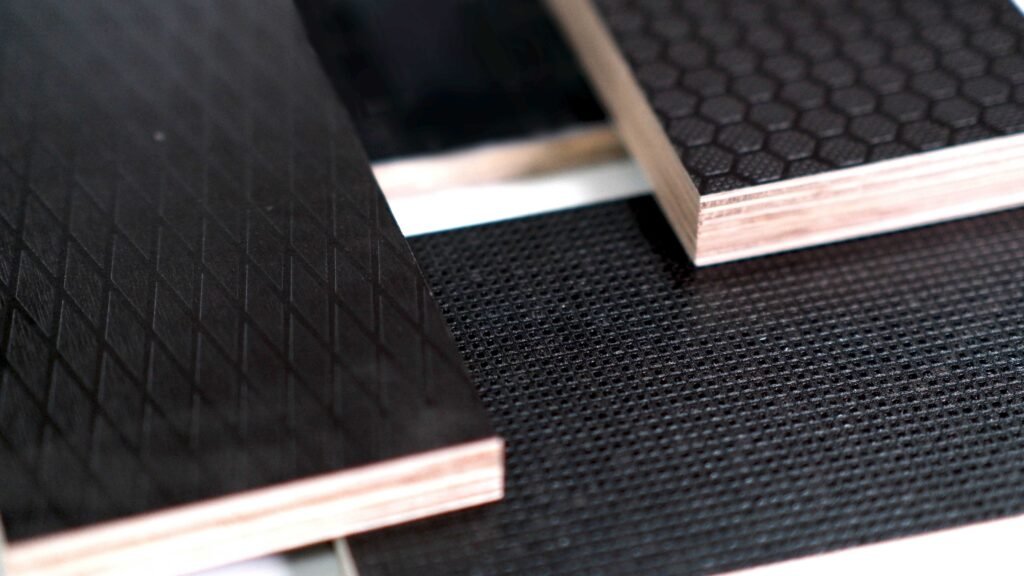
Film Faced birch plywood grade
lease select defect or grade.
- Grade I
- Grade II
- Grade III
Allowable defects
Using wood grain structure, sound knots, or inlays to communicate
Film delamination, tears, lack, or shedding
Lack of film: areas of film faced birch plywood surface not covered with film.
With a lack of film, measurement is performed along the edge only. The defective area is measured across the width, otherwise both the width and the length of the bare area are measured, and the overall defect size is defined as the ratio of the total damaged areas to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed along one edge up to 3 mm wide provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Film overlaps (folds)
Film overlap: local thickening due to film overlap on the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed up to 500 mm wide, up to 10 mm long, mo more than 1 pc/m2.

Film pieces sticking
Film pieces sticking: glued pieces of film stuck to the plywood surface during lamination.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed up to 30×30 mm, or up to 10×100 mm, mo more than 1 pc/m2.

Core veneer defect traces: knot holes, other holes
Core veneer defect traces: film damage following the core veneer defects (knots, holes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed up to 25×25 mm, mo more than 1 pc/m2.

Trace of spliced or jointed veneer
Trace of spliced or jointed veneer: an imprint on the surface of film faced plywood due to the use of spliced or jointed veneer.
Measured by width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed with no coating damage.

Press plate lines and stains
Press plate lines and stains: lines or stains on the surface of film faced plywood due to press plate contamination.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total contaminated regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Film lines and stains
Film lines and stains: discolored areas on the surface of film faced plywood caused by volatile emissions during pressing.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total discolored regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed up to 15% of the sheet’s area.
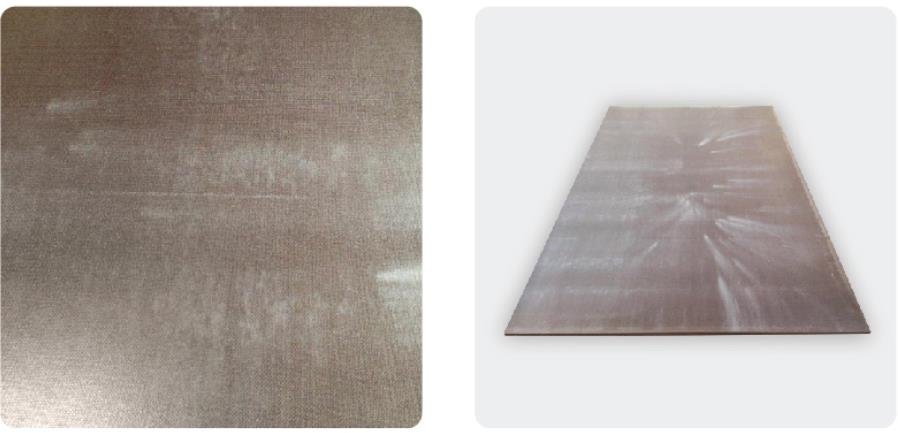

Press plate imprints
Press plate imprints: blows caused by laminate press plate defects.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed up to 5% of the sheet’s area.
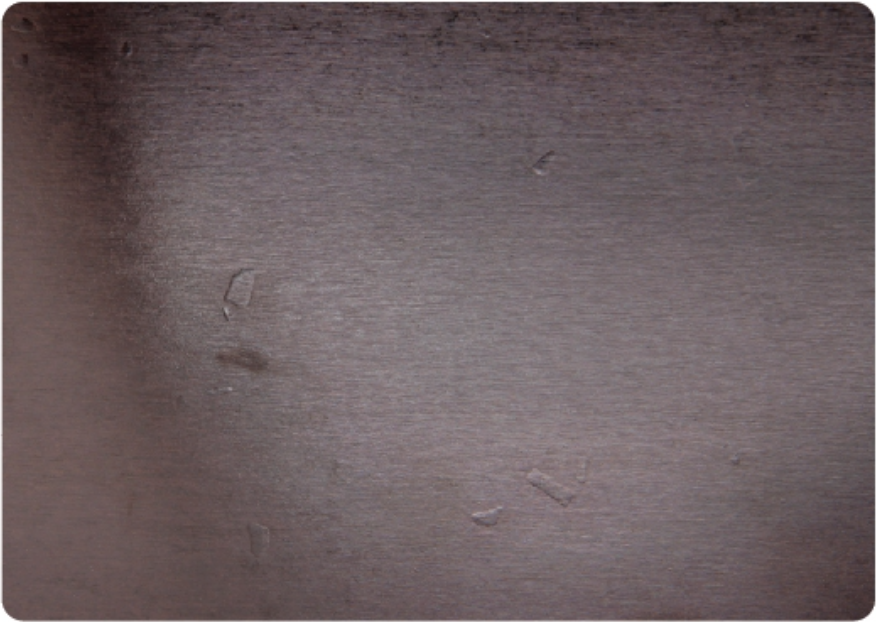

Indentation
Indentation: local face veneer indentation with no coating damage
Indentation depth is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 6 mm in diameter, max. 1 pc/m2 provided that the film is fast to the plywood.

Cutting defects, shears at the edge
Cutting defects, shears at the edge: defect involving lack of film coating along the plywood sheet’s edge.
Defect length is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 3 mm long provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Paint drips
Paint drips: paint splashes on the plywood sheet’s face.
Measured by width.
Allowable
Allowed up to 5 mm wide.
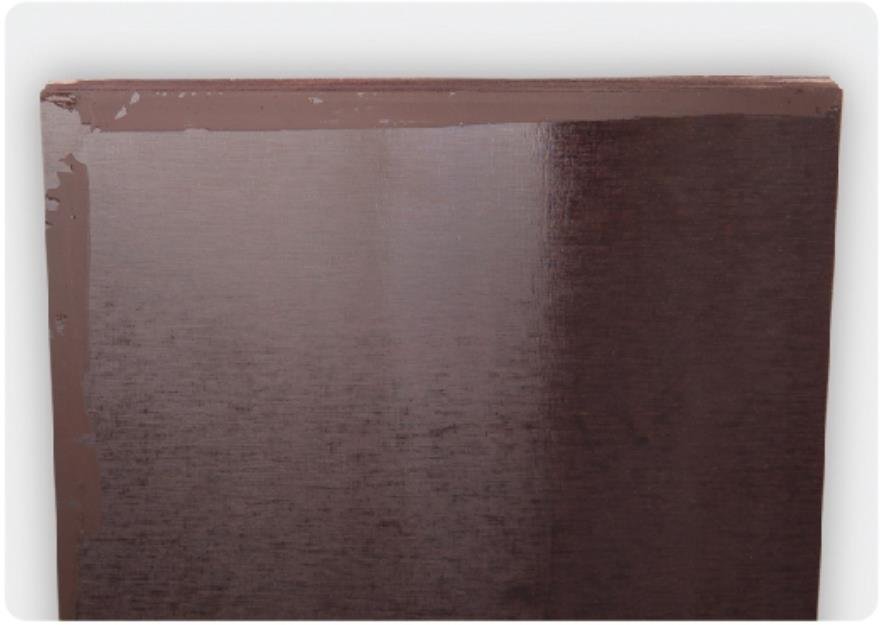

Warping
Warping: bowing of the plywood sheet.
Measured by putting a ruler diagonally against the sheet that rests on a flat surface, and gaging its maximum deflection.
Allowable
Ignored in plywood up to 6.5 mm thick, allowed in plywood over 6.5 mm thick with deflection up to 15 mm per 1 mm of the sheet’s diagonal length.

Not allowable defects
Temperature stain marks
Stain marks on the surface: film discoloration (with or without coating damage) due to premature drying without pressure.
Defined as a grading factor.
Not allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: shakes, damage, knot holes
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage following the face veneer defects (knots, holes, shakes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Not allowable
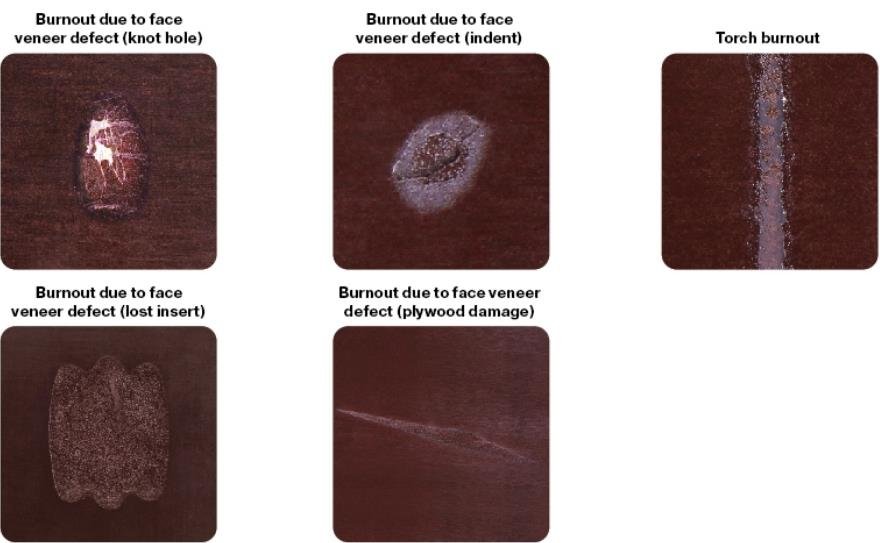
Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: coarse peeling
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage in the surface indents resulting from local wood removal during processing.
Measured by the length and the width of the area occupied, expressed as a percentage of the total sheet area.
Not allowable
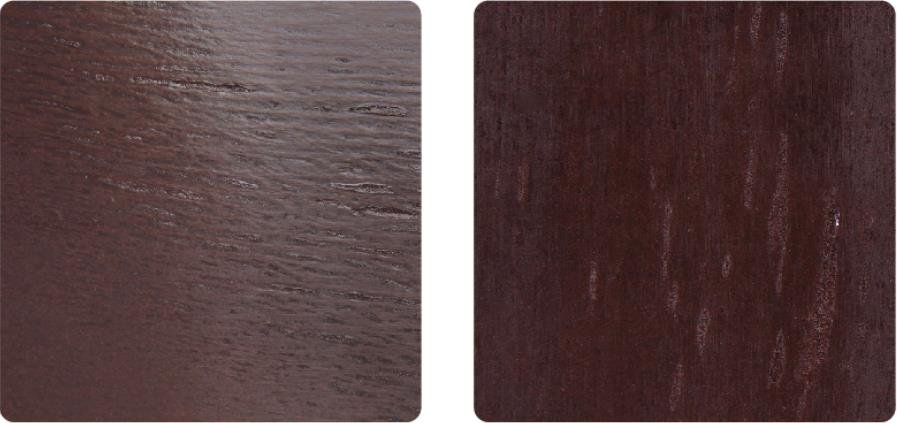

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: lines or stains due to sanding
Sanding lines: film damage because of variations in plywood thickness.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Not allowable

Local blisters on plywood surface
Local blisters on plywood surface: partial film delamination from the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Not allowable

Veneer particles glued into the face veneer
Veneer particles glued into the face veneer: veneer particles glued into the face veneer before lamination.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Not allowable
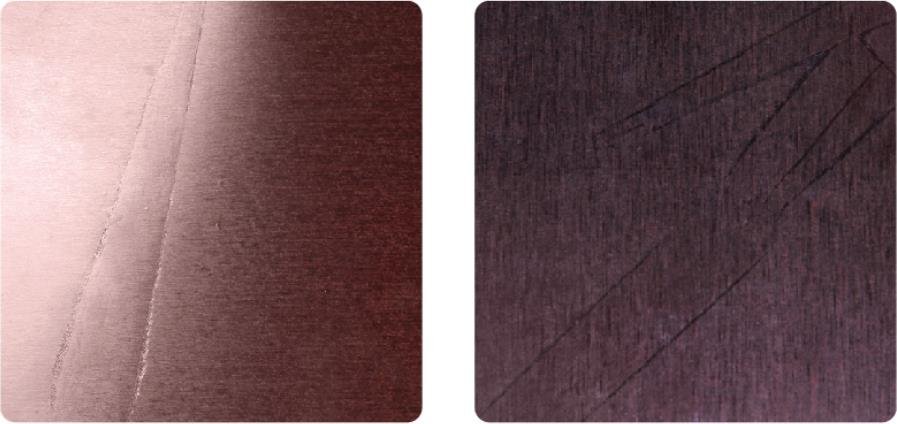

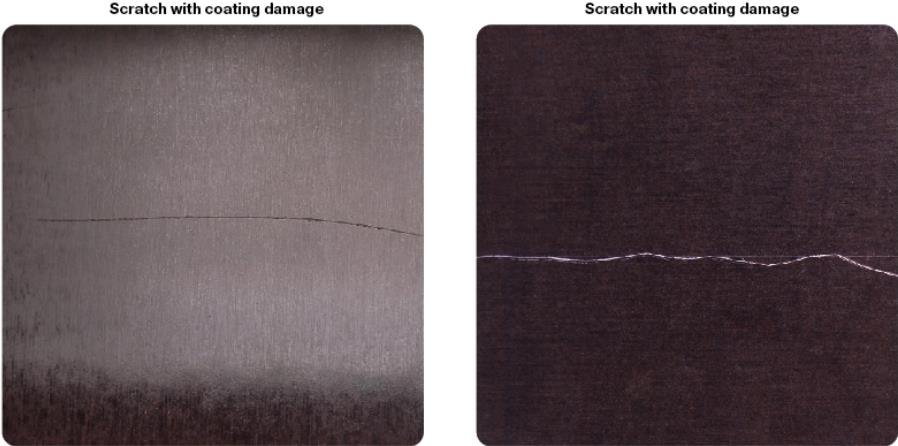
Scratches
Scratches: film faced plywood coating damage with a sharp object in the form of a long narrow recess or a local face veneer indenting with film damage.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Not allowable
Veneer shortage
Veneer shortage: defect involving a partial lack of core veneer, except for the front knots and cracks.
Measured by depth.
Not allowable
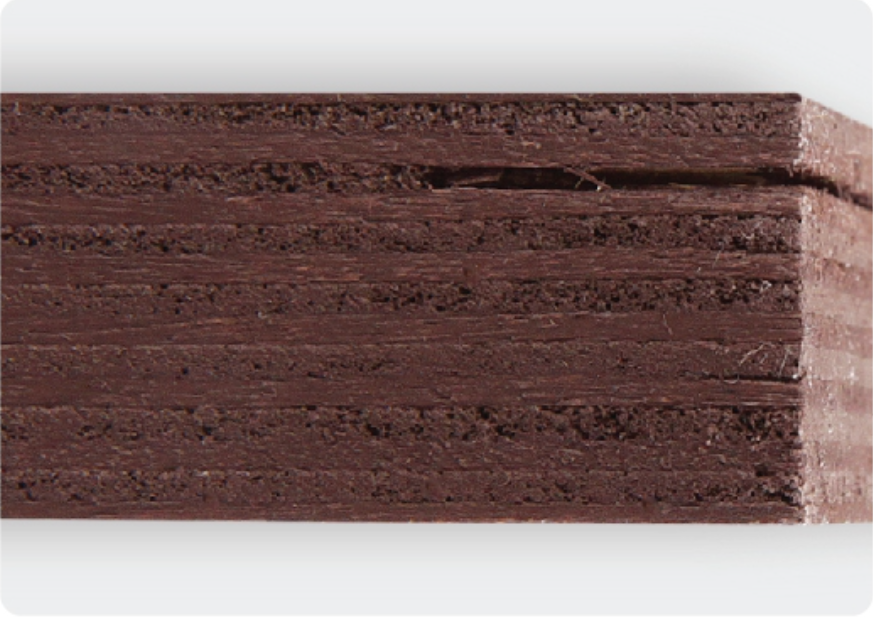

Local core veneer delamination (hidden blister)
Delamination: separation of two adjacent veneers along the glueline.
Defined as a grading factor.
Not allowable

Allowable defects
Using wood grain structure, sound knots, or inlays to communicate
Telegraphing wood grain structure, wood flaws: contours of sound knots, wood grain structure, inserts on the surface of film faced birch plywood.
Defined as a grading factor.
Allowable

Film delamination, tears, lack, or shedding
Lack of film: areas of film faced birch plywood surface not covered with film.
With a lack of film, measurement is performed along the edge only. The defective area is measured across the width, otherwise both the width and the length of the bare area are measured, and the overall defect size is defined as the ratio of the total damaged areas to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed along one edge up to 3 mm wide provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Temperature stain marks
Stain marks on the surface: film discoloration (with or without coating damage) due to premature drying without pressure.
Defined as a grading factor.
Allowable
Allowed unless the film is damaged.

Film overlaps (folds)
Film overlap: local thickening due to film overlap on the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Film pieces sticking
Film pieces sticking: glued pieces of film stuck to the plywood surface during lamination.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: shakes, damage, knot holes
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage following the face veneer defects (knots, holes, shakes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: coarse peeling
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage in the surface indents resulting from local wood removal during processing.
Measured by the length and the width of the area occupied, expressed as a percentage of the total sheet area.
Allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: lines or stains due to sanding
Sanding lines: film damage because of variations in plywood thickness.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed up to 25% of the sheet’s area.

Core veneer defect traces: knot holes, other holes
Core veneer defect traces: film damage following the core veneer defects (knots, holes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Core veneer defect traces: open split, shakes
Core veneer defect traces: film damage following the core veneer defects (open split, shakes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Trace of spliced or jointed veneer
Trace of spliced or jointed veneer: an imprint on the surface of film faced plywood due to the use of spliced or jointed veneer.
Measured by width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Press plate lines and stains
Press plate lines and stains: lines or stains on the surface of film faced plywood due to press plate contamination.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total contaminated regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Film lines and stains
Film lines and stains: discolored areas on the surface of film faced plywood caused by volatile emissions during pressing.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total discolored regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Local blisters on plywood surface
Local blisters on plywood surface: partial film delamination from the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed up to 100 mm in diameter, no more than 1 pc/m2.

Veneer particles glued into the face veneer
Veneer particles glued into the face veneer: veneer particles glued into the face veneer before lamination.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Allowable

Press plate imprints
Press plate imprints: blows caused by laminate press plate defects.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Indentation
Indentation: local face veneer indentation with no coating damage
Indentation depth is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 0.5 mm deep with no coating damage.

Scratches
Scratches: film faced plywood coating damage with a sharp object in the form of a long narrow recess or a local face veneer indenting with film damage.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Allowable
Allowed with no coating damage.

Cutting defects, shears at the edge
Cutting defects, shears at the edge: defect involving lack of film coating along the plywood sheet’s edge.
Defect length is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 10 mm long provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Paint drips
Paint drips: paint splashes on the plywood sheet’s face.
Measured by width.
Allowable

Veneer shortage
Veneer shortage: defect involving a partial lack of core veneer, except for the front knots and cracks.
Measured by depth.
Allowable
Allowed along one edge, max. 5 mm deep.

Warping
Warping: bowing of the plywood sheet.
Measured by putting a ruler diagonally against the sheet that rests on a flat surface, and gaging its maximum deflection.
Allowable
Ignored in plywood up to 6.5 mm thick, allowed in plywood over 6.5 mm thick with deflection up to 15 mm per 1 mm of the sheet’s diagonal length.

Not allowable defects
Local core veneer delamination (hidden blister)
Delamination: separation of two adjacent veneers along the glueline.
Defined as a grading factor.
Not allowable

Allowable defects
Using wood grain structure, sound knots, or inlays to communicate
Telegraphing wood grain structure, wood flaws: contours of sound knots, wood grain structure, inserts on the surface of film faced birch plywood.
Defined as a grading factor.
Allowable

Film delamination, tears, lack, or shedding
Lack of film: areas of film faced birch plywood surface not covered with film.
With a lack of film, measurement is performed along the edge only. The defective area is measured across the width, otherwise both the width and the length of the bare area are measured, and the overall defect size is defined as the ratio of the total damaged areas to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed along one edge up to 3 mm wide provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Film pieces sticking
Film pieces sticking: glued pieces of film stuck to the plywood surface during lamination.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Temperature stain marks
Stain marks on the surface: film discoloration (with or without coating damage) due to premature drying without pressure.
Defined as a grading factor.
Allowable
Allowed unless the film is damaged.

Film overlaps (folds)
Film overlap: local thickening due to film overlap on the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: coarse peeling
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage in the surface indents resulting from local wood removal during processing.
Measured by the length and the width of the area occupied, expressed as a percentage of the total sheet area.
Allowable

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: lines or stains due to sanding
Sanding lines: film damage because of variations in plywood thickness.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable
Allowed up to 25% of the sheet’s area.

Burnt film (burnouts) due to face veneer defects: shakes, damage, knot holes
Burnt film (burnouts): film damage following the face veneer defects (knots, holes, shakes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Core veneer defect traces: open split, shakes
Core veneer defect traces: film damage following the core veneer defects (open split, shakes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Core veneer defect traces: knot holes, other holes
Core veneer defect traces: film damage following the core veneer defects (knots, holes, etc.).
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Trace of spliced or jointed veneer
Trace of spliced or jointed veneer: an imprint on the surface of film faced plywood due to the use of spliced or jointed veneer.
Measured by width, expressed in mm.
Allowable

Press plate lines and stains
Press plate lines and stains: lines or stains on the surface of film faced plywood due to press plate contamination.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total contaminated regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Film lines and stains
Film lines and stains: discolored areas on the surface of film faced plywood caused by volatile emissions during pressing.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total discolored regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Local blisters on plywood surface
Local blisters on plywood surface: partial film delamination from the plywood surface.
Measured by length and width, expressed in mm.
Allowable
Allowed up to 100 mm in diameter, no more than 1 pc/m2.

Veneer particles glued into the face veneer
Veneer particles glued into the face veneer: veneer particles glued into the face veneer before lamination.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Allowable

Press plate imprints
Press plate imprints: blows caused by laminate press plate defects.
Measured by the length and the width and defined as the ratio of the total damaged regions area to the overall plywood sheet’s area (expressed as a percentage).
Allowable

Indentation
Indentation: local face veneer indentation with no coating damage
Indentation depth is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 0.5 mm deep with no coating damage.

Scratches
Scratches: film faced plywood coating damage with a sharp object in the form of a long narrow recess or a local face veneer indenting with film damage.
Their occurrence is considered as a grading factor.
Allowable
Allowed with no coating damage.

Cutting defects, shears at the edge
Cutting defects, shears at the edge: defect involving lack of film coating along the plywood sheet’s edge.
Defect length is measured.
Allowable
Allowed up to 10 mm long provided that the area is coated with moisture protective paint.

Paint drips
Paint drips: paint splashes on the plywood sheet’s face.
Measured by width.
Allowable

Veneer shortage
Veneer shortage: defect involving a partial lack of core veneer, except for the front knots and cracks.
Measured by depth.
Allowable
Allowed along one edge, max. 5 mm deep.

Warping
Warping: bowing of the plywood sheet.
Measured by putting a ruler diagonally against the sheet that rests on a flat surface, and gaging its maximum deflection.
Allowable
Ignored in plywood up to 6.5 mm thick, allowed in plywood over 6.5 mm thick with deflection up to 15 mm per 1 mm of the sheet’s diagonal length.

Local core veneer delamination (hidden blister)
Delamination: separation of two adjacent veneers along the glueline.
Defined as a grading factor.
Allowable

Different surface film faced birch core plywood sheet