How does laser wood engraving work?
Laser wood engraving is a precise and versatile process that uses a focused laser beam to etch designs, patterns, text, or images onto the surface of wood. This technology allows for highly detailed and intricate engravings with consistent results.

Here’s how laser wood engraving works:
- Laser Source: Laser engraving machines are equipped with a laser source, typically a CO2 laser or a fiber laser. The choice of laser type depends on the specific application and the type of laser wood being engraved. CO2 lasers are commonly used for engraving wood, as they provide excellent control and precision.
- Focused Laser Beam: The laser source emits a highly concentrated and focused beam of light. This beam of light is directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to ensure it remains focused on the wood surface.
- Wood Preparation: Before engraving, the wood surface must be properly prepared. This typically involves sanding the wood to achieve a smooth and even surface. Some wood types may also benefit from the application of a wood finish or masking tape to reduce scorching or discoloration during the engraving process.
- Setting Parameters: The operator of the laser engraving machine uses software to create or import the design or artwork that will be engraved onto the wood. Within the software, various parameters are set, including the laser power, speed, and resolution. These settings control the depth and intensity of the engraving.
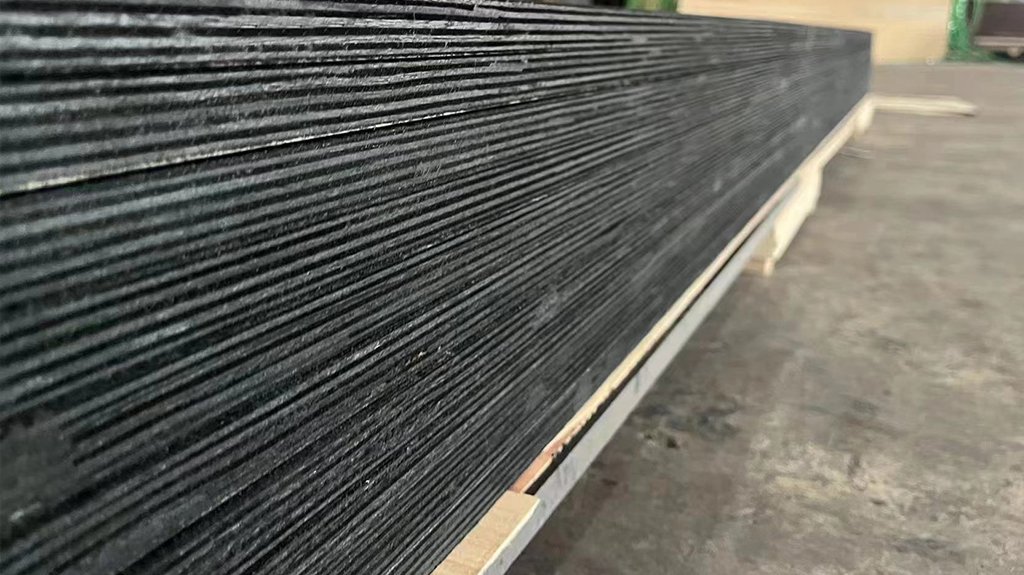
- Engraving Process: Once the wood is prepared, and the parameters are set, the laser engraving machine is activated. The focused laser beam follows the designated path determined by the digital design. As the laser beam interacts with the wood surface, it vaporizes or burns away a thin layer of material, creating the engraved pattern or text.
- Resolution and Detail: Laser wood engraving is known for its high resolution and ability to capture fine details. The beam can create intricate patterns, text as small as a few millimeters in height, and intricate designs with smooth curves.
- Depth Control: The depth of the engraving can be controlled by adjusting the power and the number of passes made by the laser. Deeper engravings require higher power and multiple passes.
- Scorching and Discoloration: Depending on the type of wood and the laser parameters, there may be some scorching or discoloration on the engraved edges. Proper parameter settings and surface preparation can minimize this effect.
- Cooling and Ventilation: Laser engraving machines often incorporate cooling systems to prevent the laser source from overheating during prolonged use. Adequate ventilation and exhaust systems are essential to remove fumes and ensure operator safety.
- Quality Inspection: After the engraving is completed, the wood surface is inspected for quality. Any residual smoke or debris is usually cleaned from the engraved area.

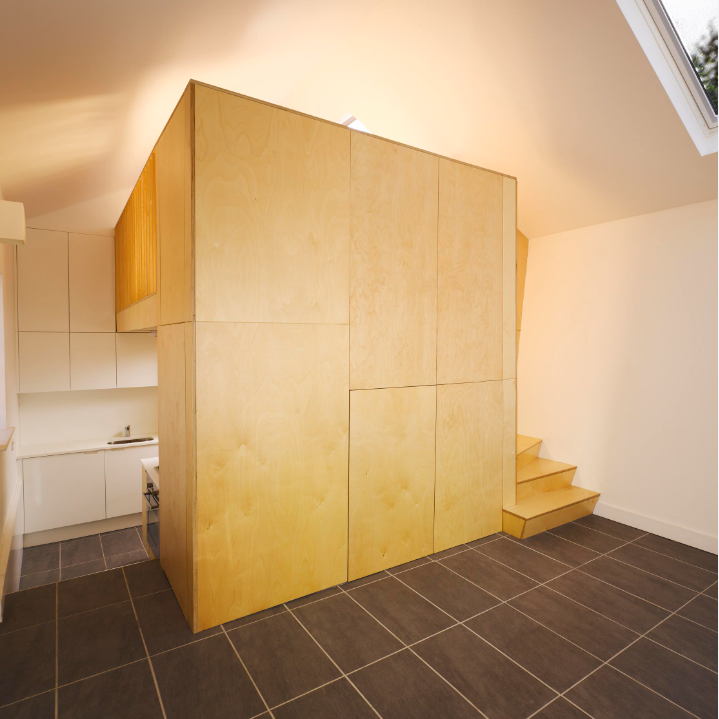
Foresmate’s Laser wood engraving is widely used for various applications, including custom signage, personalized gifts, woodworking projects, decorative panels, and more. Its precision, speed, and ability to replicate intricate designs make it a popular choice for adding detailed and customized elements to wood surfaces. Additionally, laser engraving is a non-contact process, which minimizes the risk of damaging the wood during the engraving process.